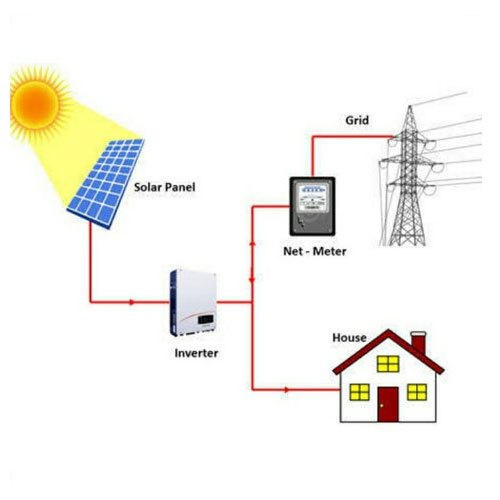
On Grid Solar System
An on-grid solar system, also known as a grid-tied or grid-connected solar system, is a photovoltaic (PV) system that is connected to the utility grid. Here are some key points about on-grid solar systems:
1. **Connection to the Grid**: Unlike off-grid systems that operate independently, on-grid systems are connected to the local electricity grid. This allows them to draw electricity from the grid when solar generation is insufficient (e.g., at night or during cloudy days) and to feed excess electricity back into the grid when production exceeds demand.
2. **Components**:
– **Solar Panels**: Convert sunlight into electricity (DC).
– **Inverter**: Converts DC electricity from the solar panels into AC electricity that can be used in homes and fed into the grid.
– **Metering**: Usually, there are two types of metering:
– **Net Metering**: Tracks both electricity consumed from and supplied to the grid, allowing homeowners to offset their electricity bills.
– **Feed-in Tariffs**: Some regions offer payments for electricity fed into the grid, providing additional income to solar system owners.
3. **Advantages**:
– **Cost Savings**: Reduces electricity bills by generating power from sunlight.
– **Environmental Benefits**: Reduces carbon footprint by using renewable energy.
– **Grid Stability**: Helps in stabilizing the grid by providing additional electricity during peak demand periods.
4. **Disadvantages**:
– **Dependence on Grid**: No power generation during grid outages for safety reasons (unless a backup system is installed).
– **Initial Cost**: Upfront costs for installation and equipment.
– **Regulatory and Policy Dependence**: Net metering policies and feed-in tariffs can vary and affect financial benefits.
5. **Installation and Maintenance**: Installation requires professional expertise to ensure proper sizing, positioning of panels, and compliance with local regulations. Routine maintenance includes cleaning panels and checking system performance.
6. **Popularity and Future**: On-grid systems are popular in urban areas where grid infrastructure is reliable and feed-in tariffs are attractive. They play a significant role in transitioning to renewable energy sources and reducing dependence on fossil fuels.
Overall, on-grid solar systems are a viable option for homeowners and businesses looking to reduce energy costs and contribute to sustainable energy practices, provided local regulations and grid infrastructure support such installations.